1 Namespaces and prefixes
This document describes nodes that belong to different namespaces. All nodes that do not belong to the NULL namespace are give a prefix in order to distinguish them. The following table assigns a namespace URI to each prefix used in this document:
| Prefix | Namespace URI | Corresponding standard |
|---|---|---|
| sch | http://purl.oclc.org/dsdl/schematron | ISO Schematron |
| sqf | http://www.schematron-quickfix.com/validator/process | Schematron QuickFix |
| xsl | http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform | XSLT 2.0 |
2 Terminology
- Schematron assertion
Condition which is declared by the Schematron elements
sch:reportorsch:assert.A failed Schematron assertion produces a Schematron error. One Schematron assertion can produce multiple Schematron errors.
- Schematron rule
According to the Schematron element
sch:rule. It contains one or more Schematron assertions.- Context
The context of a Schematron rule is defined by the attribute
context. If a rule matches to more than one node, it has more than one context.
- Schematron error
A Schematron error occurs if a Schematron assertion failed for one context of its Schematron rule.
- Context
The context of the Schematron error is the node, which was matched by the Schematron rule, when the Schematron assertion failed.
The attribute
subjecthas no affect to the context of the Schematron error. Unlike to the context of the Schematron rule, the Schematron error has only one context node.
3 Introduction
This section describes the classification of the based concepts of Schematron QuickFix.
3.1 Fix
A fix is a change of a document, applied to an occurred error. All changes must have the object to solve this error. Requirement is to detect the error first.
3.2 Quick fix
A Quick fix is a fully automatic implemented fix. In connection with an error (produced by a validation of a document) one ore more Quick fixes are offered to execute. A user can choose the Quick fix, which is executed by a fully automated process.
A Quick fix requires:
Instructions, written in a document processing language, to implement the fix. The instructions have to designed in a way, that it is able to process them applied to a context. The context is defined by the occurred error.
A human-readable description of the Quick fix. The description should be displayed to the user, when he chooses the Quick fix.
It is able to define Quick fixes inside of a validation parser or using a therefore designed script language. First, there is a limited quantity of Quick fixes, in the second case the quantity is unlimited.
It depends on the quantity of unique kinds of errors from the validation language, which way makes more sense. Is the quantity of kinds of errors limited, an implementation of Quick fixes inside of the parser is possible.
Basic requirements for an implementation of a Quick fix workflow:
Definition of Quick fixes (embedding into a parser or into a validation language).
A workflow to execute the Quick fixes.
Graphical user interface to choose the Quick fixes.
4 Workflow
Schematron QuickFix (SQF) is an extension of the validation language Schematron to embed Quick fixes. To provide an overview of the Schematron QuickFix concept, this section describes the integration of SQF into the Schematron workflow.
Note:
Please note the different spelling of QuickFix and Quick fix. The spelling QuickFix means a Quick fix of the extension language Schematron QuickFix. The spelling Quick fix means a nonspecific Quick fix, which was described in the section Quick fix.
The following figure shows the SQF workflow in eight steps:
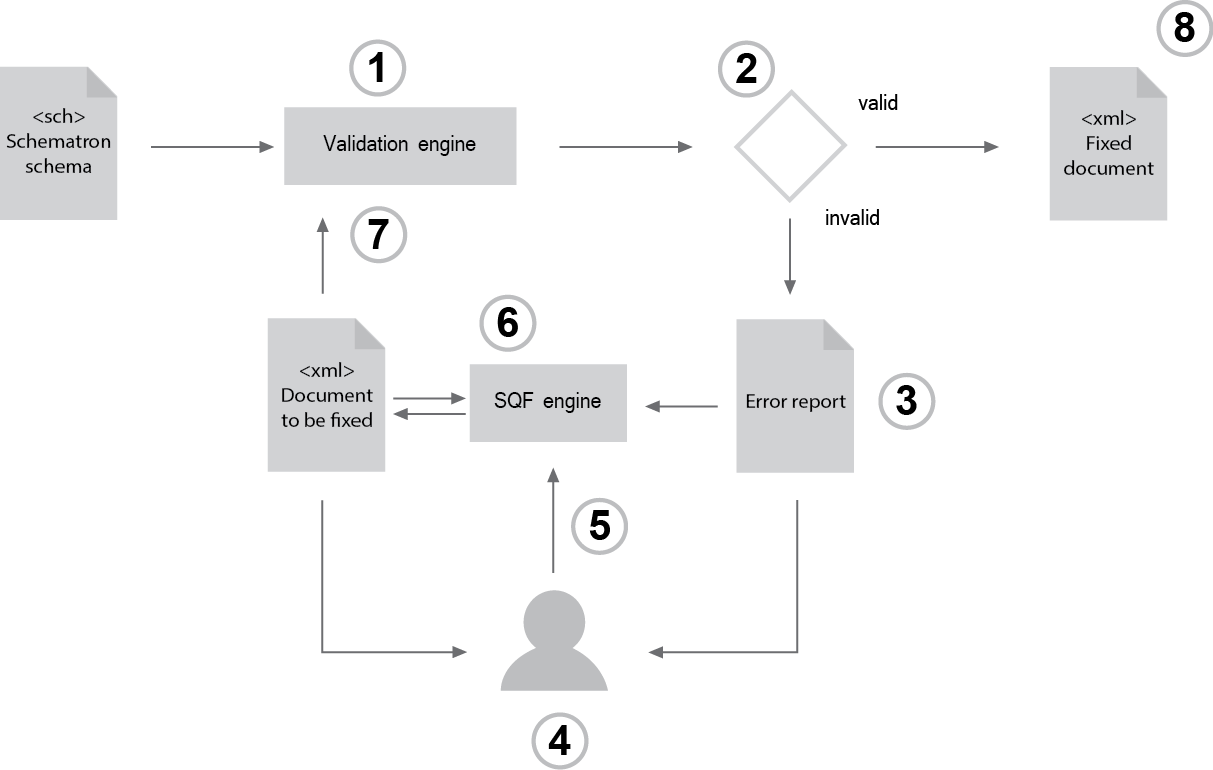
The following sections describes each step of the workflow diagram and its difference to the conventional Schematron workflow.
4.1 Schematron validation
The workflow starts with a classic Schematron validation process. There are no changes needed for Schematron QuickFix, but a preferred way to implement the QuickFixes is, to compile them during the basic Schematron validation.
For this specification, the following terms will be used to describe the documents, which are subject of this step:
- Source document
The document, which is validated. If there are multiple documents, which are connected by using XInclude, these documents will be considered as one document. If there are multiple documents, which will be validated to one Schematron schema (for instance during a validation of documents of a folder), this validations will be considered as multiple separated validations.
- Schematron schema
The source document will be validated against the Schematron schema. If there are multiple schematron documents, which are connected by include techniques of Schematron, these documents will be considered as one document. If there are multiple schematron schemas are associated with the source document (for instance by more than one
xml-modelprocessing instructions), the validations by each schema will be considered as multiple separated validations.
4.2 Validation result check
The second step is the validation result check. If the validation result is true, the source document is valid and the next step is step 8. If the validation result is false, there are errors detected.
In this step, there is no changes for Schematron QuickFix necessary.
4.3 Error report
The error report should be generated by the Schematron validation. The implementation is free to use a proprietary or a standardised structure for this report (SVRL for example).
In this step, changes for Schematron QuickFix are not needed, but it is a possible way, to implement Schematron QuickFix, by extending the SVRL or any other maybe existing report structure, so the report is able to contain the compiled QuickFixes.
4.4 Show the errors in the source document
The last step of the classic Schematron validation workflow is, to display the detected errors, by using the error message in connection with the context of the Schematron error.
A required change for Schematron QuickFix is, to display the available QuickFixes for those errors, in relation to the Schematron error.
4.5 Decision of the user
The Schematron QuickFix user should have an interactive option to select one or more QuickFixes to execute it. This is a new step for Schematron QuickFix only.
4.6 Executing a Quick fix
Depending on the decision of the user, the selected QuickFix(es) will be executed. Normally the source document will be the source of this fix process and will be replaced by the result of this process. But the implementation could support QuickFixes for external documents (See example in Appendix). In this cases each external document will be the source of a separate fix process and replaced by the result.
This is also a new step for Schematron QuickFix only.
4.7 Validation after the fix
After each execution of a QuickFix, a new validation of the changed document is necessary to update the error report or to get a positive validation result. This is equal to a new Schematron validation in a classic Schematron workflow, which is necessary if there are any changes on the source document.
5 Language
This section describes the meanings of the Schematron QuickFix syntax.
5.1 Embedding into Schematron
To embed Schematron QuickFix into Schematron, all extending elements should have
the namespace http://www.schematron-quickfix.com/validator/process
(preferred prefix sqf).
The following table shows the permitted parent-child relations between the namespaces of SQF and Schematron.
| Parent element | Permitted children |
|---|---|
sch:schema |
|
sch:rule |
|
sqf:title
|
|
sqf:p |
|
sqf:fix |
|
The following table shows which attributes from the SQF namespace should be permitted of which Schematron elements:
| Schematron element | Permitted SQF attribute |
|---|---|
sqf:assert |
|
sqf:report |
|
5.2 QuickFix
A QuickFix requires the following properties:
Description with at least a title
ID
One or more change commands (see Change commands)
A QuickFix is able to have the following additional properties:
Additional documentation as a part of the description
Condition to provide the QuickFix
Loop to make the QuickFix generic (see Generic QuickFix)
User Entry to parametrise the QuickFix (see User Entries)
Note:
Please note that the properties does not need to be declared directly in the
corresponding sqf:fix element, but could also be adopted of other
QuickFixes by calling them (sqf:call-fix element).
5.2.1 Definition of a QuickFix
The QuickFix is defined by the sqf:fix element. The requirements
will be satisfied with the following base structure:
<sqf:fix id="fix1">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>Fix 1</sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
[Elements from the content model (sqf:delete | sqf:add | sqf:replace | sqf:stringReplace | sqf:call-fix)+]
</sqf:fix>The defined QuickFix above has the following properties:
Description / title: Fix 1
ID: fix1
One or more change commands: not specified yet.
5.2.2 QuickFixes ID
The ID of the QuickFix and the QuickFix groups is the Identifier to reference QuickFixes and QuickFix groups.
Requirements to set the ID:
The ID has to correspond with the XSD type xs:NCName.
Inside of a Schematron rule the ID must be unique.
Global QuickFixes or QuickFix groups should not have the same IDs.
In the following cases it is permitted that two QuickFixes, QuickFix groups or a QuickFix and a QuickFix group have the same IDs:
Both are local, but declared in different Schematron rules.
5.2.3 Global and local QuickFixes
A QuickFix or a QuickFix group
can be defined global or
local. Local QuickFixes or QuickFix groups are declared inside
of the Schematron rule and only the
assertions of this rule are able
to refer to the QuickFixes or QuickFix
groups. Global QuickFixes or QuickFix groups are declared inside of the
sqf:fixes element and available for all Schematron assertions (see below Scope).
Example for a global QuickFix:
<sch:schema>
[...]
<sqf:fixes>
<sqf:fix id="fix2"> [...] </sqf:fix>
</sqf:fixes>
</sch:schema>Example for a local QuickFix:
<sch:rule context="[...]">
[...]
<sqf:fix id="fix1"> [...] </sqf:fix>
</sch:rule>5.2.4 Reference to a QuickFix
Schematron assertions are able to
refer to one or more QuickFixes or QuickFix groups or a mix of QuickFixes and QuickFix groups. Therefore the
sqf:fix attribute contains a whitespace separated list of
IDs. Each ID has to refer to an ID of a QuickFix or QuickFix group. The amount of
references are unbounded, but implementations are able to set a limit.
The sch:assert element refers to the QuickFixes with the ID
"fix1" and "fix2":
<sch:assert test="[...]" sqf:fix="fix1 fix2">[...]</sch:assert>
<sqf:fix id="fix1">
[...]
</sqf:fix>
<sqf:fix id="fix2">
[...]
</sqf:fix>5.2.4.1 Scope
Schematron assertions are only able to refer to QuickFixes or QuickFix groups which are in scope of its Schematron rules.
A local QuickFix or QuickFix group is in scope, if its
sqf:fixorsqf:groupelement is a descendent element of the samesch:ruleelement as the referring Schematron assertion.A global QuickFix or QuickFix group is in scope of any Schematron rules of the Schematron Schema, except there is a local QuickFix or QuickFix group with the same ID in the scope of the Schematron rules.
It is an error, if a Schematron assertions refers to a QuickFix or QuickFix group, which is not in the scope of its Schematron rules.
5.2.4.2 Providing conditions
Is a Schematron assertion producing a Schematron error that refers to a QuickFix, a Schematron QuickFix implementation may provide the QuickFix as a choice for the user to execute the QuickFix in connection to the occurred error.
Exceptions:
A QuickFix, which condition was not satisfied in the context of the Schematron error, should not be provided.
A generic QuickFix may not able to be provided in some cases (see Generic QuickFix section)
It is up to the implementation to provide QuickFixes which has no change commands or uses elements which are not supported by the implementation.
5.2.4.3 Default QuickFix
The sqf:default-fix attribute is provided to set a default
QuickFix for a Schematron
assertion. The attribute value should be the id of a
QuickFix.
It is an error, if the default
QuickFix is not referred by the Schematron
assertion (using the sqf:fix attribute).
An implementation is free, how to handle the default QuickFix.
5.2.5 Execution of a QuickFix
During the execution process of a QuickFix each change command will be executed in the context node of the error, if their condition was satisfied in this context.
5.2.5.1 Execution of more than one QuickFix
It is free to the implementation to allow executions of more than one QuickFix at once. But an execution of more than one QuickFix of the same Schematron error at once are not permitted.
It is up to the implementation to warn the user against possible conflicts or to hide QuickFixes to avoid such conflicts.
5.2.6 QuickFix group
A QuickFix group is a set of one
or more QuickFixes. The QuickFix will be implemented with the
sqf:group element. Additional it needs an ID, specified by a
mandatory id attribute.
A Schematron assertion is able to refer to a QuickFix group on the same way it refers to a QuickFix. A reference to a QuickFix group is equal to references to all QuickFixes which the QuickFix group contains.
The QuickFix group has the ID groupid and contains the QuickFixes with the IDs fix1 and fix2.
The first sch:assert element refers to the QuickFixes fix1
and fix2 per QuickFix ID. The second one refers to the same
QuickFixes per ID of the QuickFix
group.
<sch:assert test="[...]" sqf:fix="fix1 fix2">[...]</sch:assert>
<sch:assert test="[...]" sqf:fix="groupid">[...]</sch:assert>
<sqf:group id="groupid">
<sqf:fix id="fix1"> [...] </sqf:fix>
<sqf:fix id="fix2"> [...] </sqf:fix>
</sqf:group>For more information see the sqf:group definition in the SQF reference.
5.2.7 Generic QuickFix
A generic QuickFix is different from a regular QuickFix in that it is defined for an unbounded count of provided QuickFixes. The count of provided QuickFixes may depend on the context of the Schematron error.
To create a generic QuickFix, the sqf:fix element gets a
use-for-each attribute. The use-for-each attribute
expects an XPath expression. For each returned value or item of the XPath
expression a QuickFix should be provided to the user. The XPath expression
will be evaluated in the context of the
Schematron error.
The XPath expression of the use-for-each attribute does not change
the context of the generic QuickFix. To access to the currently returned
item/value, a build-in XPath variable $sqf:current (in the SQF
namespace) should be provided. The $sqf:current variable should
be available in each XPath expression inside of the sqf:fix
element, which has an use-for-each attribute.
It should be an error, if the $sqf:current variable was used in
a sqf:fix element, which does not have an use-for-each
attribute.
Example:
<sqf:fix id="generic-fix" use-for-each="//*[@id]">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>Delete element <value-of select="$sqf:current/@id"/></sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
<sqf:delete match="$sqf:current"/>
</sqf:fix>For each element in the document which has an id attribute
the implementation should provide one QuickFix. The title of those
QuickFixes should be the fix string "Delete element " concatenated
with the value of the corresponding id attribute. The
change command will be, to delete the corresponding element.
5.2.7.1 Maximum number of provided QuickFixes
Please note, that it will be easy to create a high number of QuickFixes for each Schematron error using this structure. To handle this, an implementation is free to set a limit of allowed providing QuickFixes for generic QuickFixes. If a generic QuickFix violates this limit, the implementation is free to do not provide any QuickFixes or to occur an error.
5.2.8 Role
The role is a meta data of the QuickFix. The role of a QuickFix describes the type of change which it makes. There are five types of changes:
"add"
The QuickFix adds nodes to the source document.
"delete"
The QuickFix deletes nodes in the source document.
"replace"
The QuickFix replace nodes from the source document by new nodes.
"stringReplace"
The QuickFix replace parts of text nodes in the source document by new nodes.
"mix"
This is a fallback role type, if the QuickFix do more things or no type of change matches to the QuickFix.
An implementation is free to support other additional roles. There are two ways to define the role of a QuickFix:
Automatically – the implementation detects the role by the contained Activity Elements. The implementation is free to define own criteria to detect the role type.
Manually – the developer overwrite the role manually using the
roleattribute:<sqf:fix id="replaceAtttribute" role="replace"> [...] <sqf:add match="*[@id]" target="id" node-type="attribute" select="generate-id()"/> </sqf:fix>The implementation may detect the role type "add", because the
sqf:addelement was used only. But the developer knows, that this QuickFix will replace the value of theidattribute anytime, so he set the role manually.
5.3 Change commands
A QuickFix needs at least one change command. A change command is implemented by
an activity element (see element group sqf:activityElements). A
change command is processed relative to an anchor node.
5.3.1 Anchor node
The anchor node is the context of a change command. By default the context of the Schematron error is the anchor node.
To specify anchor nodes, the match attribute is provided to each
activity element. If an activity element points to more than one anchor
node, for each anchor node the change command will be executed. If an
activity element points to no anchor node, no change command will be
executed.
The match attribute expects an XPath expression. The context of
relative expressions is the context of the
Schematron error. It is recommended to allow expressions which
can use the full functionality of XPath 2.0 (or newer) and additionally the
XSLT 2.0 functions.
5.3.1.1 Requirements of the Anchor node / match attribute
The only restriction to the XPath expression of the match attribute, is
that the type of the return value needs to be node()*. Any
return values which does not match to this type should occurs an
error.
An implementation is free to set further restrictions to the XPath expressions. If a Change command violates this restrictions, the implementation is free to occurs an error, to hide the corresponding QuickFixes or to do not execute those Change commands, but any other of the corresponding QuickFix.
Note:
Please note, that supporting any XPath 2.0/XSLT 2.0 functionality could have affects to the workflow: If one of the returned nodes changes the document context, the fix process should respect this.
5.3.2 Conditions
Each change command can have a condition to execute. Therefore the attribute
use-when is provided to each activity element. The condition
will be defined in the context of the
Schematron errors. If the condition is not satisfied the
change command should not be executed.
5.3.3 Create new content
Depending of the kind, the change command may create new content to insert it into or replace nodes from the source document. There are three ways to create new content:
5.3.3.1 By the attributes node-type and target
To create a new node, the change command may provide the attributes
node-type and target. This attributes create
exact one node.
To create a new node the attribute node-type provides the
following values:
"keep"
To create a node from the same type as the anchor node.
"element"
To create an element.
"attribute"
To create an attribute
"processing-instruction" or "pi"
To create a processing instruction
"comment"
To create a comment
Bellow a list of restrictions to use the node-type and target attribute:
If the
node-typeattribute has not the value "comment", the attributetargetis required. It sets the name of the created node. The value of thetargetattribute will be interpreted as an attribute value template. The effective value should be valid to the XSD type xs:QName.If an Activity Element has a target attribute, the
node-typeattribute is required.
To create the value or content of the new node, you need to respect the following terms:
If the
node-typeattribute has the value "element" (or "keep" and the anchor element is an element), the content of the new element will be created by XPath or by the content of the Activity Element.If the
node-typeattribute has the values "attribute", "processing-instruction", "pi" or "comment" (or "keep" and the anchor node is not an element), the value of the new node will be created by XPath or by the content of the Activity Element. If this returns nodes, the value will be created by the values of this nodes. More than one node value will be joined to one node value separated by whitespace.
5.3.3.2 By an XPath expression
To define the new content by an XPath expression, the select
attribute is provided. The select attribute can be combined with the
attributes node-type and target. In this case the XPath expression of
the select attribute detects the content or value of the new node.
Otherwise the XPath expression creates new content in the following
way:
If the XPath expression returns an atomic value, the value will be transformed into an text node.
If the XPath expression returns a sequence of atomic values, all values will be transformed to a text node. The values will be separated by whitespace.
If the XPath expression returns one or more nodes, the nodes will be copied into the source document (see below Copy nodes).
If the Activity Element has a select attribute, the element
content should be empty.
5.3.3.3 By the Activity Element content
The content of the Activity Elements has the same functionality as the
content of xsl:template elements from the XSLT 2.0
Recommendation. This means:
Elements from the XSLT namespace will be processed in the context of the change command. If XSLT elements are able to change the context in XSLT, this should have the same effect to there descendents in SQF.
Elements which not belong to the XSLT, SQF or Schematron namespace will be processed as Literal Result Elements.
Extensions of the XSLT template behavior:
Elements from the SQF namespace will be processed as it is defined in this specification. Permitted element is:
sqf:copy-ofTo copy existing nodes into the source document (see below Copy nodes).
Elements from the Schematron namespace will be processed as it is defined in the Schematron specification. Permitted elements are:
sch:letsch:value-ofsch:name
The XSLT instruction
xsl:apply-templatesshould be handled as if there is a copy templates defined (see below Copy nodes).
5.3.3.4 Copy nodes
There are three ways to copy nodes:
If the XPath expression of the
selectattribute of an Activity Element returns one or more nodes, these nodes will be copied.With the
sqf:copy-ofelement (as content of an Activity Element) nodes can be copied. Aselectattribute defines by an XPath expression the nodes to be copied. The default value of theselectattribute is "node()".If the XSLT instruction
xsl:apply-templatesis used as content of an Activity Element, the applied nodes should also be copied. The implementation is free to do a full copy of the applied nodes or to respect change commands caused by other (or the same) executed QuickFixes. (See example in Appendix)
5.3.4 Conflicts
A conflict is thrown, if there are more than one change command for the same anchor node, during an QuickFix execution. There are two kinds of conflicts:
Resolvable conflict
If the conflict is between two or more change commands which belongs to the same QuickFix, the conflict is resolvable. In this case, the change command will be executed, whose activity element is defined at first inside of the
sqf:fixelement.Warning raised conflict
If two or more change commands from different QuickFixes are in conflict, the conflict is not resolvable. A warning should be produced. The implementation is free to decide which QuickFix has higher priority. This kind of a conflict is just possible, if an implementation allows to execute more than one QuickFix at once.
5.3.5 Kind of the change commands
There are four predefined kinds of change commands:
Add
Delete
Replace
StringReplace
A Schematron QuickFix implementation is free to provide extending Change
commands. The extending change commands should provide the attributes of the
attribute group activityBase and
respect the concepts to create new
content.
5.3.5.1 Add
Creates one or more nodes and insert it relative to the anchor node as new content. The new content could be created by the SQF attributes, by XPath or by the content of the sqf:add element.
The position attribute detects the position relative to the anchor node, where the new content should be inserted. The following values are available:
- first-child
If the anchor node is an element the new content will be inserted after the start tag of the anchor node.
If the anchor node is an attribute, the new content will be inserted after the start tag of the parent element of the anchor node.
Otherwise: the new content will be inserted after the anchor node.
This value is the default value of the
positionattribute.- last-child
If the anchor node is an element the new content will be inserted before the end tag of the anchor node.
If the anchor node is an attribute, the new content will be inserted before the end tag of the parent element of the anchor node.
Otherwise: the new content will be inserted after the anchor node.
- before
The new content will be inserted before the anchor node.
If the anchor node is an attribute, the new content will be inserted before the parent element of the anchor node.
- after
The new content will be inserted after the anchor node.
If the anchor node is an attribute, the new content will be inserted after the parent element of the anchor node.
The position attribute is useless, if the new content are one
or more attributes. In this case, the new content should always be added
as attribute(s) of the anchor node.
In the case, the new content is an attribute, it is an error if the anchor node is not an element.
If the anchor node is an element and has an attribute with the same name as one of the new attributes, the new attributes should replace the existing attributes.
5.3.5.3 Replace
The anchor node will be replaced by new content. The new content can be created by the SQF attributes, by XPath or by the content of the sqf:replace element.
It is an error, if the new content is an attribute, but the anchor node not.
5.3.5.4 StringReplace
The anchor node has to be a text node. To analyze the text node, the
regex attribute is required. The value of the
regex attribute will be interpreted as an attribute value template. The effective value should be
a valid Regular
Expression corresponding to the XSLT 2.0
Recommendation.
To control the interpretation of the Regular Expression, a
flags attribute should be available. The value of the
flags attribute will be interpreted as an attribute value template. The effective value should be
interpreted the same way, as the XQuery 1.0 and
XPath 2.0 Functions and Operators Recommendation
specifies the $flags parameter of Regular Expression
functions.
Any substrings, which matches to this Regular Expression, will be replaced by new content. The new content can be created by XPath or by the content of the sqf:stringReplace element.
5.4 Variables
5.4.1 Declaration
The Schematron QuickFix specification does not provide an own structure to declare variables for the XPath expressions. There are two permitted ways do declare variables:
Using Schematron variables (
sch:let).Using XSLT variables (
xsl:variable).
There is no difference between this ways, though the XSLT variables provides
more functionality (e.g. as attribute, value by content). There
should be no change of the original functionality by using these variable
structures for Schematron QuickFix.
5.5 Parameter
There are two different ways to use parameters for QuickFixes:
Default parameter: The default parameter is a common parameter to reuse and parametrize the QuickFix. Therefore the reused QuickFix may contains parameter(s) (see chapter Declaration). Another QuickFix may call the reused QuickFix (see chapter Call a QuickFix). During the call, the calling QuickFix is able to set the value of the parameters of the reused QuickFix.
Abstract parameter: This parameter is to declare the usage of Schematron parameters inside of the QuickFix, which should be defined by the
sch:paramelement.
The following sections should discuss the default parameter. The abstract parameter will be discussed in the section Abstract parameter only.
5.5.1 Declaration
The declaration of a parameter has to be at the beginning of the
sqf:fix element, before any other elements. The sqf:param
element declares one parameter. To declare multiple parameter you need
multiple sqf:param elements.
5.5.1.1 Name
The name attribute is the only required attribute of the
sqf:param element. It sets the name of the parameter.
It is an error, if there is an other parameter inside of
the sqf:fix element with the same name.
The value of the name attribute should to be valid to the type xs:QName.
5.5.1.2 Default value
The default value of the parameter will be set by the default
attribute. The attribute value needs to be a valid XPath expression. The
parameter will have the returned value, if the value is not set by the
call of this fix (see chapter Call a
QuickFix).
If the default attribute is omitted, the default value is a
zero length string.
5.5.1.3 Type
If the type attribute is set, it specifies the required type
of the parameter value. If the type attribute is omitted, the
type of the parameter value is unspecified. The implementation is free
to support proprietary or a standardised types. The types needs to be
referred by a valid xs:QName.
5.5.1.4 Required parameters
A parameter is by default optional. If the call-fix do not specify a value for an optional parameter, the default value will be used. The required attribute with the value "yes" indicates that the parameter value needs to be specified by the call-fix.
It is an error, if the default attribute is
not omitted, though the required attribute has the value
"yes".
5.5.2 Call a QuickFix
There are different use cases to call a QuickFix. In any case the
sqf:call-fix element should be used:
Reuse the change commands of one QuickFix, specified by parameters.
Combine the change commands of QuickFixes by multiple QuickFix calls.
Add specific change commands to a QuickFix by mixing Activity Elements with one or more QuickFix calls.
Specify a description to the called QuickFixes or reuse the description of the called QuickFix.
All use cases could be combined as well. If a QuickFix has multiple QuickFix calls or a mix of one QuickFix call and one or more Activity Elements, a specific description (sqf:description element) is mandatory. The reuse of the description of a called QuickFix is only permitted, if the calling QuickFix contains exactly one QuickFix call.
To call a QuickFix, the sqf:fix element of the calling QuickFix may
contain a sqf:call-fix element at any position. The only condition
is, that it is after any sqf:param and sqf:description
elements. The sqf:call-fix element should have a mandatory
ref attribute. Its value should refer to an ID of any
available QuickFix. The referred QuickFix will be called.
If the calling QuickFix is a global QuickFix, only other global QuickFixes or
QuickFixes of global
QuickFix groups are available.
If the calling QuickFix is local, any QuickFix is available, which is available for any
assertion in the scope of the calling QuickFix. Additionally if there is a
local QuickFix which
has the same ID as a global QuickFix, the local QuickFix may refer to
the global QuickFix by containing a sqf:call-fix element with a
ref attribute which refers to the ID of it self.
It is permitted, to call a QuickFix inside of a generic QuickFix.
It should be occurred an error, if the called QuickFix is a generic QuickFix.
5.5.2.1 Specify a parameter
A sqf:call-fix element may contain one or more
sqf:with-param elements. Each sqf:with-param
element set a value of one parameter of the called QuickFix. The
mandatory name attribute determines which parameter of the
called QuickFix will be specified. The type of the name
attribute needs to be a valid xs:QName.
It is mandatory, that in the called QuickFix a parameter is declared
which have the same name as the name attribute of the
sqf:with-param element.
The value of the parameter will be defined the same way as the values of XSLT
2.0 variables or parameters, though it is no
as attribute available.
5.5.2.2 Adoption of properties
If a QuickFix calls another QuickFix, the calling QuickFix will adopt
some kind of properties in any case, some properties only if there is no
property from the same kind set for the calling QuickFix and other
properties will be never adopted. If a QuickFix adopt a property, it is,
as if the calling QuickFix obtained this property by itself. If the
order of the property elements is significant (for instance the order of
the Activity Elements), the effective position will be determinate by
replacing all sqf:call-fix elements by the adopted property
elements.
The following properties of the called QuickFix will be adopted in any case:
Any change command (defined by Activity Elements)
User Entry to parametrise the QuickFix (see User Entries)
Any other property of the above kinds, which may be adopted by another QuickFix call.
The following properties will be adopted conditionally:
Description:: title and additional documentation
An adoption of the description is permitted only, if the calling QuickFix calls exactly one QuickFix and does not contains any Activity Element. Otherwise a specific description for the calling QuickFix is mandatory.
The description of the called QuickFix will be adopted, if the calling QuickFix has no description.
Condition to provide the QuickFix
The condition to provide will be adopted only, if the calling QuickFix calls exactly one QuickFix, does not contain any Activity Element and has no specific
use-whenattribute.Any other property of the above kinds, which may be adopted by another QuickFix call and satisfies the conditions described above.
The following properties will not be adopted in any case:
ID
It is an error, if the called QuickFix has the following property:
Loop to make the QuickFix generic (see Generic QuickFix)
Note:
Please note, that it is permitted, to call a QuickFix inside of a generic QuickFix.
5.5.3 Example
<sqf:fix id="call-fix">
[...]
<sqf:call-fix ref="reused-fix">
<sqf:with-param name="param1" select="10"/>
</sqf:call-fix>
</sqf:fix>
<sqf:fix id="reused-fix">
<sqf:param name="param1" default="'defaultValue'" type="xs:string"/>
<sqf:param name="param2" required="yes" type="xs:integer"/>
[...]
</sqf:fix>5.5.4 Abstract parameter
5.5.4.1 Declaration
A sch:param element from a
QuickFix with the value of the abstract attribute set to
"true" is defined as an abstract parameter of the
QuickFix. As the default
parameter, the abstract parameter declaration must be at
the beginning of an sqf:fix element.
A QuickFix referred from an abstract pattern must declare all abstract
pattern parameters used by it. A sch:param element, with the value of the
abstract attribute set to "true", must be
added for all abstract pattern parameters used in the QuickFix.
An abstract parameter defined in a QuickFix declares that the QuickFix uses a parameter of an abstract pattern. The QuickFix can be instantiate only from an abstract pattern that defines the abstract parameter. A QuickFix with one or more abstract parameters can be used only from abstract patterns.
If a QuickFix parameter that is
defined as abstract it cannot have the type,
required and default attributes. Its value
will be set form the abstract pattern instantiation.
5.5.4.2 Usage
Abstract parameters cannot be used as normal XPath variables. The reference of the abstract parameter will be replaced at instantiation by the value specified in the abstract pattern. The replacing value will be set by the instantiation of the abstract pattern according to the Schematron specification. The instantiation of the abstract pattern must specify a value for every abstract parameter of the QuickFix.
5.6 User Entry
A User Entry is a parameter for the QuickFix which can be set by the user during the runtime of the QuickFix execution.
A QuickFix can have multiple User Entries. A User Entry requires the following properties:
Title: A short description of the functionality of the User Entry
Name: To refer the User Entry value inside of the XPath expressions of the QuickFix
A User Entry is able to have the following additional properties:
Descriptions: More documentation information.
Default value: To suggest this value to the user.
Type: To restrict the possible values of the User Entry and get the value in the correct data type
5.6.1 Definition of a User Entry
User Entries have to be defined before any change commands in the
sqf:fix element:
<sqf:fix id="fix1">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>Fix 1</sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
<sqf:user-entry name="ue1">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>User Entry 1</sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
</sqf:user-entry>
<sqf:user-entry name="ue2">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>User Entry 2</sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
</sqf:user-entry>
[Elements from the content model (sqf:delete | sqf:add | sqf:replace | sqf:stringReplace)+]
</sqf:fix>Each sqf:user-entry element defines an User Entry. Consequently, the
QuickFix fix1 has two User Entries with the names
ue1 and ue2.
5.6.2 Value usage
To use the value, each User Entry can be used as an XPath variable. So the value of the User Entry can be used in each XPath expression of all Activity Elements in the User Entry. The name of the XPath variable is the name of User Entry.
<sqf:user-entry name="ue1">
<sqf:description>
<sqf:title>User Entry 1</sqf:title>
</sqf:description>
</sqf:user-entry>
<sqf:replace target="{$ue1}" node-type="element" select="$ue1"/>The Activity Element sqf:replace replaces the anchor node (context of the Schematron errors) by a
new element. The name will be set by the user by setting the User Entry
ue1. The content of the new element will be also the value
of the User Entry ue1.
5.6.2.1 Scope
The User Entry value is available in all XPath expressions of all Activity Elements of the QuickFix.
Exceptions:
There could some restrictions of the implementation, which could restrict this (for instance, restrictions to the match attribute).
5.6.3 Implementation of User Entries
A SQF implementation which supports User Entries should provide the user an interface to set User Entries after or while choosing the QuickFix. For this the titles of each User Entry should be displayed in connection with the corresponding QuickFixes.
5.6.4 Default value
The default attribute sets a default value for the User Entry, using an XPath
expression. The result value can be used by the implementation to provide a
default value to the user, when he set the User Entry. The default value
should used like the default value of a parameter (see sqf:param
element):
There are no optional User Entries.
Each User Entry should be set by the user.
The default value is to provide it as possible value only.
5.7 Embedding XPath
Schematron QuickFix is based on the W3C Recommendation XPath 2.0. Any XPath expression of the Schematron schema needs to match the syntax allowed by the XPath grammar.
5.7.1 Attributes to embed XPath expressions
The following table shows attributes, whose value will be parsed as XPath expressions, corresponding to the XPath 2.0 Recommendation:
| Attribute | Element | Context | Description | Required return type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| default | sqf:param | context of the Schematron error | Default value for the parameter | no requirement |
| sqf:user-entry | context of the Schematron error | Default value for the User Entry | no requirement | |
| match | sqf:add | context of the Schematron error | Contexts of the change commands | node()* |
| sqf:delete | context of the Schematron error | Contexts of the change commands | node()* | |
| sqf:replace | context of the Schematron error | Contexts of the change commands | node()* | |
| sqf:stringReplace | context of the Schematron error | Contexts of the change commands | text()* | |
| select | sqf:add | Anchor node | Nodes or atomic values, which should be inserted | no requirement |
| sqf:copy-of | Inherits from the parent node. | Nodes to copy | node()* | |
| sqf:replace | Anchor node | Nodes or atomic values, which should be inserted | no requirement | |
| sqf:stringReplace | Anchor node | Nodes or atomic values, which should be inserted | no requirement | |
| sqf:with-param | context of the Schematron error | Value for the parameter | no requirement | |
| use-when | sqf:add | Anchor node | Condition to process the change command | no requirement, interpreted as boolean |
| sqf:delete | Anchor node | Condition to process the change command | no requirement, interpreted as boolean | |
| sqf:replace | Anchor node | Condition to process the change command | no requirement, interpreted as boolean | |
| sqf:stringReplace | Anchor node | Condition to process the change command | no requirement, interpreted as boolean | |
| sqf:fix | context of the Schematron error | Condition to provide the QuickFix | no requirement, interpreted as boolean | |
| sqf:group | context of the Schematron error | Condition to provide all QuickFixes of this QuickFix group | no requirement, interpreted as boolean |
5.7.2 Attribute Value Template
The following table shows attributes, whose value is interpreted as attribute value template corresponding to the XSLT 2.0 Recommendation:
| Attribute | Element | Context | Effective value requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| regex | sqf:stringReplace | Anchor node | Valid Regular Expression corresponding to the XSLT 2.0 Recommendation. |
| flags | sqf:stringReplace | Anchor node | Should match to the requirements of the $flags parameter, specified in the XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Functions and Operators Recommendation |
| target | sqf:add | Anchor node | xs:QName |
| sqf:replace | Anchor node | xs:QName |
The effective value requirements should be satisfied after interpreting the attribute value template.
5.8 Localization
The SQF localization concept is based on the XML concept to detect the
natural language, using the xml:lang attribute.
Consequently, SQF elements are able to inherit the language property of all
ancestors.
5.8.1 Locatable elements
The following list shows SQF elements, which are locatable with the attribute
xml:lang:
sqf:descriptionsqf:fixsqf:fixessqf:groupsqf:psqf:titlesqf:user-entry
5.8.2 Localization of a QuickFix or User Entry
The natural language parts of a QuickFix or User Entry are defined by the elements sqf:title and sqf:p. To provide an alternative text phrase for localization (effective localization value), these elements are permitted to obtain a ref attribute. The ref attribute may refer (by reference values) to IDs or key values of one or more text phrases in the same or separate document. Multiple reference values should be separated by whitespaces.
The minimal implementation of the ref attribute should support a reference to an ID of a Schematron sch:diagnostic element. An implementation is free to support references to other text phrase formats (See example in Appendix).
If a ref attribute contains one or more reference values which cannot be resolved by the implementation, these values should be ignored. No error or warning should occurred.
A ref attribute may refer to multiple text phrases in different languages by multiple reference values or may refer by one reference value which leads to different text phrases. In any case, the implementation needs to detect the requested language, the language code of the element which contains the ref attribute (initial language) and all language codes of the referenced text phrases. The following four cases should be supported:
The requested language matches to the initial language.
In this case, the references should be ignored and the initial value of the element should be used as effective localization value.
The requested language matches to one of the referenced text phrase
In this case, the referenced text phrase, which is assigned to the requested language should be used as effective localization value.
The requested language matches to none of the given languages.
In this case, the references should be ignored and the initial value of the element should be used as effective localization value.
This case is a localization issue and should not occur. The implementation is free to throw a warning.
6 Implementation modes
A QuickFix can be implemented generally in two different modes:
Unparsed Process Mode
XSLT only mode
An implementation is free to support only one or both modes. If an implementation supports both modes, it should be a general configuration to switch between the two modes.
6.1 Unparsed Process Mode
The Unparsed Process Mode requires that no changes will be applied to the source document, which are not defined by the executed QuickFix. Changes which are caused by parsing the document and creating a new, XML identical document (skip the XML declaration, resolving default attributes, CDATA sections, etc.), should not influence the document. That is why it is not possible to implement the Unparsed Process Mode with only XSLT processes.
6.2 XSLT only mode
If an implementation is based only on XSLT processes, this is called the XSLT only mode. In this case, it is allowed to change the source document on any QuickFix execution in the following ways, though it is not defined in the QuickFix:
Skip the XML declaration
Skip the DOCTYPE declaration
Skip whitespace:
which are outside of the root element and not in processing instructions and comments.
non significant whitespace
Normalize whitespace
Leading whitespace of content in processing instructions in prolog
between attributes
Resolve default attributes to encoded attributes
Resolve CDATA sections to text nodes.
Resolve entity references.
7 Schematron QuickFix reference
7.1 Elements
7.1.1 <sqf:add>
This activity element adds a node to one or more nodes of the XML instance.
The attributes match and position define the position where the nodes will be added. The position is determined by the anchor node(s) (@match) and the insertion direction (@position).
The attributes node-type, select and target and the content of the element define the nodes to be added.
7.1.1.3 Attributes
7.1.1.3.1 @position
| Description |
The position attribute defines the position of the nodes to be added relatively to the anchor node (see @match).
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default |
If the value of the node-type attribute is "attribute", the position attribute should not be set, because the node to be added will always be inserted as attribute. Otherwise the default value is "first-child".
|
| Value |
|
7.1.1.3.2
See attribute group sqf:activityManipulate .
7.1.2 <sqf:call-fix>
This element calls another QuickFix within a QuickFix. The called QuickFix must be defined globally or for the same Schematron rule as the calling QuickFix. A calling QuickFix should not have other activity elements.
The calling QuickFix adopts the activity elements of the called QuickFix. With the help of parameters, these can be specified (see sqf:with-param ).
The description and other characteristics (e.g. @use-when) of the called QuickFix will not be adopted.
7.1.2.3 Attributes
7.1.2.3.1 @ref
| Description | This attribute refers to a QuickFix by using the ID. The referred QuickFix must be defined globally or for the same Schematron rule as the referring QuickFix. |
|---|---|
| Use | required |
| Value |
xs:string
|
7.1.2.3.2
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.3 <sqf:copy-of>
This element is available within activity elements. The function is to copy nodes selected by the select attribute. The element with its attribute is treated as xsl:copy-of with select attribute as it is defined in the XSLT requirement.
7.1.4 <sqf:delete>
This activity element deletes one or more nodes of the XML instance.
The match attribute defines the nodes to be deleted.
7.1.4.2 Attributes
7.1.4.2.1
See attribute group sqf:activityBase .
7.1.5 <sqf:description>
Adds a human readable description to the parent element.
7.1.6 <sqf:fix>
Defines a Schematron QuickFix with its content. All commands will be processed if the QuickFix is activated by the user.
7.1.6.3 Attributes
7.1.6.3.2 @role
| Description | With this attribute the role of the QuickFix can be set manually. The role of a QuickFix describes the type of change which it makes. If the role is not set manually, the role is the type of the used activity element ("add", "delete", "replace" or "stringReplace"). If two different activity elements are used in a QuickFix, the role is automatically "mix". |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
|
7.1.6.3.3 @use-for-each
| Description | QuickFixes with use-for-each attribute are generic. Each return value of the evaluated XPath expression should create an own QuickFix. To access to the current return value, the XPath variable $sqf:current should be provided. |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "." |
| Value |
xs:string
|
7.1.6.3.4 @use-when
| Description | The condition to provide the QuickFix. |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "true()" |
| Value |
xs:string
|
7.1.6.3.6
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.7 <sqf:fixes>
Contains globally useable Schematron QuickFixes and QuickFix groups.
7.1.7.2 Attributes
7.1.7.2.3
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.8 <sqf:group>
Defines a Schematron QuickFix group. If the group is linked by an assert or report, all QuickFixes of this group will be associated with the assert/report.
7.1.8.3 Attributes
7.1.8.3.2 @use-when
| Description | The condition to provide the QuickFixes of the QuickFix group. |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "true()" |
| Value |
xs:string
|
7.1.8.3.4
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.9 <sqf:p>
Paragraph within a description.
7.1.9.3 Attributes
7.1.9.3.2
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.9.3.3
See attribute group sqf:refAttribute .
7.1.10 <sqf:param>
This element defines a parameter for a QuickFix. The parameter can be used like a variable within the QuickFix. The value can be set by the sqf:with-param element.
The content defines a default value for the parameter.
7.1.10.1 Exception
Abstract parameters (see attribute abstract) cannot be used as normal XPath variables. An abstract parameter declares, that the current QuickFix uses a parameter of an abstract pattern. A QuickFix with one or more abstract parameters can be used just by abstract patterns. The value of the parameter will be set by the instantiation of the abstract pattern according to the Schematron specification. The instantiation of the abstract pattern must specify a value for every abstract parameter of the QuickFix.
7.1.10.3 Attributes
7.1.10.3.1 @abstract
| Description |
This attribute sets for the parameter whether it is abstract or not.
The current quick fix can be instantiate only from an abstract pattern that defines this abstract parameter. Inside of a global QuickFix every used parameter of an abstract pattern must be declared by an abstract parameter.
If a parameter is defined as abstract, it can not have a type, required or default attribute. Its value will be only form the abstract pattern instantiation.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "false" |
| Value |
xs:boolean
The value "true" is used for abstract parameter, "false" for regular parameter.
|
7.1.10.3.2 @required
| Description |
This attribute sets for the parameter whether it is optional or required.
If the parameter is required, it cannot have a default attribute or any content.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "no" |
| Value |
|
7.1.10.3.3
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.10.3.4
See attribute group sqf:parameterAttributes .
7.1.11 <sqf:replace>
This activity element replaces one or more nodes of the XML instance by a node. The activity command combines the delete and the add command.
The nodes to be deleted are defined by the match attribute. The nodes to be added are defined by the attributes node-type and select and the content of the sqf:replace element.
The position of the nodes to be added is the position of the nodes to be deleted.
7.1.11.3 Attributes
7.1.11.3.1
See attribute group sqf:activityManipulate .
7.1.12 <sqf:stringReplace>
This activity element replaces substrings of text nodes by other nodes. The text nodes are defined by the match attribute. The regex attribute defines the substrings of the text nodes.
The nodes to be inserted are defined by the content of the sqf:stringReplace element or the select attribute. Note: The context within the sqf:stringReplace element is set to the substrings. So, it is an atomic value.
7.1.12.3 Attributes
7.1.12.3.1 @flags
| Use | optional |
|---|---|
| Value |
xs:string
Flags to control the interpretation of the regular expression (given in the regex attribute). The flags can be specified by XPath expressions which are marked by curly brackets. After processing, the flags must meet the requirements of the flags attribute of the xsl:analyze-string element.
|
7.1.12.3.2 @regex
| Use | required |
|---|---|
| Value |
xs:string
Regular expression. The expression can be specified by XPath expressions which are marked by curly brackets. After processing, the regular expression must meet the requirements of the regex attribute of the xsl:analyze-string element.
|
7.1.12.3.3 @select
| Description |
The select attribute defines nodes or an atomic value as the nodes to be inserted. If the select attribute is set, the sqf:stringReplace element should be empty.
The selected nodes will be copied. Unlike a deep copy function, the copied nodes could be manipulated by the current or other activity elements.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default |
There is no default value. If the select attribute is not set, the content of the activity element defines the nodes to be inserted.
|
| Value |
xs:string
XPath expression. The context of relative expressions is the substring to replace.
Note: The context will be always an atomic value. To select nodes from the XML instance, the use of variables outside of the sqf:stringReplace element is necessary.
|
7.1.12.3.4
See attribute group sqf:activityBase .
7.1.13 <sqf:title>
Name of a QuickFix or a user entry.
7.1.13.3 Attributes
7.1.13.3.2
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.13.3.3
See attribute group sqf:refAttribute .
7.1.14 <sqf:user-entry>
Defines a user entry. With the help of the user entry, the user can interact with the QuickFix. The user entry refers to a sqf:param element. The value of the parameter is set manually by the user. The implementation should provide the user entry when the user selects the QuickFix.
7.1.14.3 Attributes
7.1.14.3.2
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.1.14.3.3
See attribute group sqf:parameterAttributes .
7.1.15 <sqf:with-param>
With the help of this element, QuickFix calls can be specified. A sqf:with-param element refers to a parameter of the called QuickFix.
The content or the select attribute define the value of the parameter. If there is content, the sqf:with-param element should not have a select attribute.
7.1.15.2 Attributes
7.1.15.2.2 @select
| Description |
This attribute defines with a XPath expression the value of the parameter. If the attribute is set, the sqf:with-param element must be empty.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:string
Must be a valid XPath expression.
|
7.1.15.2.3
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.2 Element groups
7.2.1 sqf:activityElements
An activity element defines a change command for one or more nodes of the instance element. This change command is specified by the kind of activity element, the content and several attributes.
7.2.2 sqf:fixElements
Elements to define QuickFixes or QuickFix groups inside of a Schematron schema.
7.2.5 sqf:templateElements
This element group describes the content of the activity elements. The behavior is similar to the content of the xsl:template element. Additionally, the elements sch:value-of and sch:let are treated as xsl:value-of and xsl:variable. Also the
sqf:copy-of
element is available.
7.3 Attribute groups
7.3.1 activityBase
7.3.1.2 Attributes
7.3.1.2.1 @match
| Description |
The match attribute defines anchor nodes for an activity element.
For each selected anchor node, the command of the activity element will be executed. For each execution, the context will be set to the anchor node.
Exception: The match attribute of the
sqf:stringReplace
element should only select text nodes.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "." By default the anchor node is the context node of the related Schematron rule. |
| Value |
xs:string
XPath expression. The context of relative expressions is the context of the related Schematron rule.
|
7.3.1.2.2 @use-when
| Description | A condition for the action of the activity Element. The action will just be executed, if the condition returns true. |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default | "true()" |
| Value |
xs:string
|
7.3.1.2.3
See attribute group sch:foreign .
7.3.2 activityManipulate
7.3.2.2 Attributes
7.3.2.2.1 @node-type
| Description |
The node-type attribute defines the node type of the nodes to be added. The attribute is required, if the target attribute is set.
If the node-type value is missing, the activity element should not have a target attribute. In this case the nodes to be added will be defined by the activity elements content or select attribute.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
|
7.3.2.2.2 @select
| Description |
The select attribute defines nodes or an atomic value as the content of the node to be added. If the select attribute is set, the activity element should be empty.
The selected nodes will be copied into the node to be added. Unlike a deep copy function, the copied nodes could be manipulated by the current or other activity elements.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Default |
There is no default value. If the select attribute is not set, the content of the activity element defines the content of the nodes to be added.
|
| Value |
xs:string
XPath expression. The context of relative expressions is the anchor node.
|
7.3.2.2.3 @target
| Description |
This attribute defines the name of the node to be added. The attribute is required if the node-type attribute is specified and the value is not "comment".
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:string
A string to define a node name. The string can be specified by XPath expressions which are marked by curly brackets. After processing, the name must be valid to the XML Schema type xs:QName.
Prefixes must be attached to a namespace in the current context of the Schematron schema. Names without prefixes will be attached to the namespace declared by the sqf:default-namespace element or to the null namespace.
|
7.3.2.2.4
See attribute group sqf:activityBase .
7.3.3 messageAttributes
Attributes to assign one or more QuickFixes to a Schematron assert or report.
7.3.3.1 Attributes
7.3.3.1.1 @default-fix
| Description |
This attribute sets a default QuickFix for the Schematron assert or report. The default QuickFix must also be referred by the sqf:fix attribute.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:string
The ID of a QuickFix which is referred by the sqf:fix attribute.
|
7.3.3.1.2 @fix
| Description | This attribute refers to one or more QuickFixes which should be assigned to the Schematron assert or report. Each referred QuickFix must be defined globally or locally for the same Schematron rule. The reference works with the ID of the QuickFix. If there is a local and a global QuickFix having the same ID, the local QuickFix will be selected. |
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:string
A list of IDs of the referred QuickFixes separated by white space.
|
7.3.4 parameterAttributes
7.3.4.2 Attributes
7.3.4.2.1 @default
| Description |
This attribute defines a default value for a parameter or User Entry by using a XPath expression. If the attribute is set to a sqf:param element, the element must be empty.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:string
Must be a valid XPath expression.
|
7.3.5 refAttribute
7.3.5.2 Attributes
7.3.5.2.1 @ref
| Description |
References to alternative text phrases (e.g. for localisation).
A minimum implementation for this attribute should support a reference to an ID of a sch:diagnostic element. Alternatively an implementation is free to support references to other localisation files (e.g. Java properties files). A reference token which does not reference to a known target should not occur an error but should be ignored.
|
|---|---|
| Use | optional |
| Value |
xs:NMTOKENS
A whitespace separated list of tokens which represents a reference.
|